

Cosmology is the study of the Universe as a whole.
on the largest scale, the Universe appears to be relatively homogeneous (same at every point), and isotropic (same in all directions). The assumption that the Universe is homogeneous and isotropic is the cosmological principle.
HUBBLE'S LAW AND THE BIG BANG
If all the objects in the Universe started from a single point at a single time, but with different velocities, they would have travelled a distance proportional to their velocity, distance=velocity x time
Compare Hubble's law, distance = velocity x 1/Hubble's constant
so Hubble's law says that the Universe looks as though everything exploded from a single point at a time 1/H0, 11-16 billion years ago: this is the Big Bang. (Model to be refined, see below).
Note: this does not imply that there is a center of the Universe.
OLBER'S PARADOX
Why is the sky dark? If space has no end, and is uniformly filled with stars, if we look far enough in any direction, we should see a star. (More distant stars will appear dimmer, but there are more of them.)
Resolution: the Universe has a finite age, and light from the most distant stars hasn't had time to reach Earth.
COSMOLOGICAL ORIGIN OF THE HUBBLE REDSHIFT
Another way to think of the Hubble redshift: it's not that the galaxies are receding from Earth, it's that the space between Earth and the distant galaxies is increasing in size. As a photon travels from a distant galaxy towards Earth, it is stretched by the expansion of space, so when it arrives at Earth it has a longer wavelength than it had when it started.
THE 3-DEGREE BACKGROUND RADIATION (also called cosmic background radiation or microwave background radiation)
Heat of the explosion should still be detectable in the form of black-body radiation but redshifted by the expansion of the Universe to longer wavelengths (cooled) to a temperature of 3 K (microwave radio wavelengths). Predicted by G. Gamow, 1948; observed by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, 1964.
There are also slight variations in temperature of the background radiation. The largest part is due to the motion of the Earth with respect to the radiation--redshifted behind (to lower T) and blue shifted before (to higher T).
THE EARLY UNIVERSE
| TIME | TEMPERATURE | DESCRIPTION |
| <10-43 s | >1032 K | ?????? (Planck era) |
| 10-43 s | 1032 K | gravity splits from other forces |
| 10-43 to 10-35 s | Grand Unification era | |
| 10-35 s | 1028 K | Strong force splits from others. Epoch of inflation? |
| 10-35 s to 10-10 s | Electroweak era | |
| 10-10 s | 1015 K | electromagnetic force separates from others |
| 10-10 s to 10-4 s | Quark era | |
| 10-4 s | 1013 K | Quarks combine to form protons and neutrons. |
| 10-4 to 500,000 years | Radiation era | |
| 180 s | 109 K | protons and neutrons combine to form nuclei; primordial helium formed |
| 500,000 years | 3000 K | nuclei and electrons combine to form atoms |
| 500,000 years to present | Matter era |
EVIDENCE FOR THE BIG BANG THEORY
ALTERNATIVES TO THE BIG BANG THEORY
Steady State hypothesis (Hoyle and others, 1940's): as the Universe is now, it always has been and always will be. Problems:
Big Bang theory is very successful, so Steady State hypothesis is not popular any more
THE FATE OF THE UNIVERSE
The Hubble expansion is opposed by the gravitational attraction of the mass in the Universe. Is the Hubble velocity of the galaxies enough to exceed the "escape velocity" of the gravity of the Universe?
WELL, WHICH ONE IS IT?
To answer the question, we need to know:
cosmic density parameter is defined to be the fraction of the amount of mass required to halt expansion that is actually present,
0= actual density/critical density
much of the mass in the Universe is dark, so we don't know the density of the Universe.
H0 is not known very accurately either.
THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE
In cosmology, Newton's theory of gravity must be replaced with Einstein's theory of gravity, general relativity. In general relativity, the bending of the path of objects by gravitational forces is described as being due to the curvature of space. Classical tests of general relativity:
In the simplest model, discussed in the text, there is simple relationship between the fate of the universe, its curvature, and its size:
| fate | curvature | 2-D illustration | type | size |
| ends in Big Crunch | positive | sphere | closed | finite |
| expands forever | zero (flat) | plane | critical | infinite |
| expands forever | negative | saddle | open | infinite |
To summarize, if the Universe is infinite in time, it is also infinite in space; if finite in time, it is finite in space.
 New results. General relativity also includes a possible new effect called
the cosmological constant,
New results. General relativity also includes a possible new effect called
the cosmological constant,
![]() 0,
which can be either attractive like gravity or repulsive
like a pressure opposing gravity. Our text discusses what
happens if
0,
which can be either attractive like gravity or repulsive
like a pressure opposing gravity. Our text discusses what
happens if ![]() 0=0.
If
0=0.
If ![]() 0
0
![]() 0, then
we need to know three things to know the fate of the Universe:
0, then
we need to know three things to know the fate of the Universe:
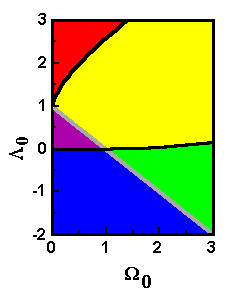
The results
are summarized in the graph to the right.
Recent
results appear to favor values near the border between
the purple and yellow areas.
Key to graph:
| area of graph | beginning | fate | curvature | size |
| red | no beginning | expands forever | positive | finite |
| yellow | Big Bang | expands forever | positive | finite |
| green | Big Bang | Big Crunch | positive | finite |
| blue | Big Bang | Big Crunch | negative | infinite* |
| purple | Big Bang | expands forever | negative | infinite* |
*If space has zero or negative curvature, the simplest model again implies
it is infinite in size; but it may also be finite. You can read more about this possibility in
an article in the 4/99 issue of
Scientific
American.
THE AGE OF THE UNIVERSE (revisited)
Our simple model that the age of the Universe = 1/H0
is not quite correct, because it assumed constant velocity -- neglecting
effects of gravity and
![]() 0.
For example, in one popular model,
0.
For example, in one popular model,
![]() 0=0
and
0=0
and ![]() 0=1,
then instead the age of the Universe is 2/3H0.
0=1,
then instead the age of the Universe is 2/3H0.
The
latest
results indicate that H0=70 km/s/Mpc ± 10%
and ![]() 0=0.3,
which would make the age of the Universe
12 to 13 billion years old (even older, if the
cosmological constant is not zero).
0=0.3,
which would make the age of the Universe
12 to 13 billion years old (even older, if the
cosmological constant is not zero).
your instructor